Data growth is estimated to double between 2022 and 2026 and with that growth in data the amount of data retained is increasing. Although NAND flash memory-based SSDs are growing in importance for storage data currently being processed (primary storage), hard disk drives are still the storage media primary used for longer term, colder, data (secondary storage). There is more data stored on HDDs than any other storage media. Although becoming less common for consumer applications and personal computers, HDDs are where most of the data in the cloud is stored.
Seagate recently officially announced the company’s 30+TB HDDs using heat-assisted magnetic recording (HAMR). The company’s Mozaic 3+ platform will provide storage densities of 3TB+ per platter. In terms of average areal density for these disk drives, that comes out to about 1.5+ TB per square inch (TB/si). This marks a new increase in HDD areal density as shown in the figure below from the Digital Storage Technology Newsletter.
When compared to a traditional PMR 16TB 3.5-inch HDD the Mozaic 3+ offers a 55% reduction in embedded carbon per terabyte and a 40% improvement in per terabyte power consumption (at 0.35W/TB). According to Seagate, they are experiencing strong demand from data center customers that are expected to complete qualification of Mozaic 3+ and move into volume ramp by end of this quarter.
A leading cloud service provider is focused on ramping of Seagate-provided drives to Mozaic 3+, reflecting their confidence in the technology. Seagate plans to expand its Mozaic (HAMR) products to 4+TB per platter by 2026 and 5+TB per platter by 2008, a 2X capacity change per disk in under 4 years as shown below.
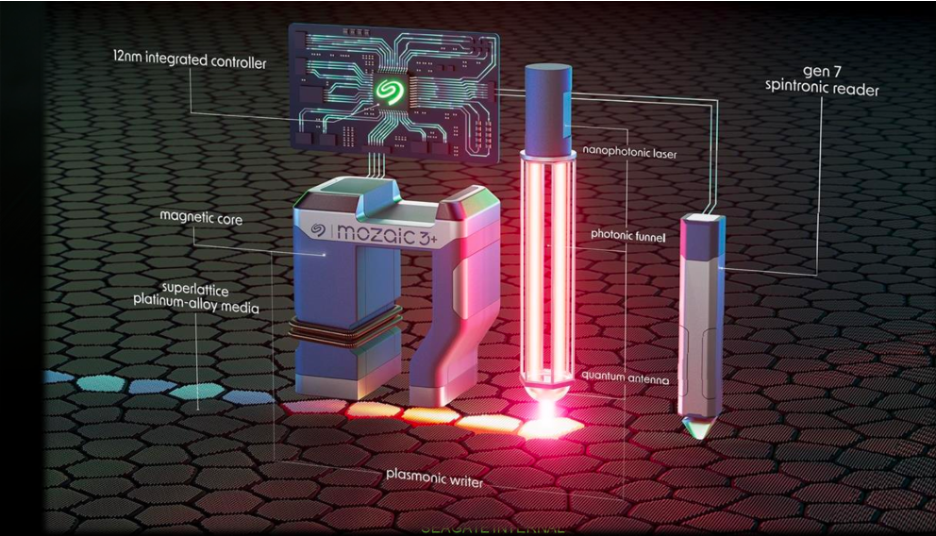
The image at the top of this article shows the various technologies that Seagate is including in its Mozaic (HAMR) HDDs. The Mozaic drives use an iron-platinum superlattice structure media, which increases the magnetic coercivity and allows for premise data writing using the plasmonic writer and results in high bit stability for smaller recorded bits.
The Plasmonic writer uses a nanophotonic laser embedded in the magnetic read/write head which produces a very small heat spot on the media enabling the write head to write on the high coercivity media. Seagate says that they plan to vertically integrate the nanophotonic laser into the plasmonic writer sub-system, allowing scaling at higher production volume.
These drives also include Seagate’s Gen 7 spintronic reader. Seagate says that this is one of the world’s smallest and most sensitive magnetic field reading sensors. Seagate has also incorporated a 12nm integrated in-house designed controller SoC delivers up to 3X the performance of previous solutions.
In addition to their use in data centers and enterprise storage systems, Mozaic 3+ HDDs will find used in video and imaging applications.
Seagate officially announced its Mozaic 30+TB HAMR-based 3.5-inch HDDs after sampling these drives with data centers and enterprise customers in 2023. This marks a new high point in HDD shipping areal densities, enabling 3TB/platters. Seagate projects that its HAMR drives will enable 40+TB HDDs by 2026 and 50+TB HDDs by 2028.
Read the full article here